Statisticians continue to publish preliminary estimates of inflation. Economists were betting ahead that the annual rate of inflation would continue to slow very gradually during February. And this was exactly confirmed. According to the preliminary estimate, consumer prices rose by 0.2 % month-on-month and 2.7 % year-on-year in February 2025. Recall that January's year-on-year inflation reached 2.8 %. Thus, this is a small slowdown in the pace of price increases.
We will have to wait until next week for definitive inflation data, when the Czech Statistical Office will publish details. However, it is already clear that inflation is being fuelled by rising food prices. Their prices are higher by 4.7 % compared to last year. This is not surprising in a situation when the annual rate of price growth in agriculture exceeds 9 %. This is bound to translate into higher final food prices.
On the other hand, energy, which had been talked about for months as a source of rising prices, contributed to the slowdown in inflation. This time, energy was down by 3.6 % year-on-year. However, even this is not surprising given that the cheapening of energy was already evident in the producer price statistics. So let us now enjoy a brief period when end-use energy prices are temporarily falling. This period is unlikely to be of long duration. While the price of electricity on the stock exchange has been stagnant over the last year plus or minus, the price of natural gas has been rising steadily since February 2024 and emission allowances will be withdrawn from circulation over the next two years.
Overall, the average inflation rate for 2024 is 2.4 %. This was its lowest level in six years. On the other hand, we were again above the 2% level that central bankers are sensitive to. Indeed, a significant number of central banks, including the Czech one and including the US Fed, have their inflation target set at 2 %. This means that the central bank actually wants our money to lose half its value every 36 years. That said, it doesn't seem like a very nice number anymore, does it?
Now imagine that this year, too, the inflation rate will end up above the Czech National Bank's 2% target on average. We estimate that the average inflation rate in 2025 will reach 2.5 %. But if - purely theoretically - inflation were to reach 2.5 % in the long term, as it probably will this year, then our savings would lose half their value every 29 years. And if inflation consistently reached 5 %, then our savings would lose half their value every 15 years. 5% inflation may seem like a lot, but at this point we've already talked about the fact that reported inflation is roughly half of what we actually perceive in our wallet. So basing it on 5% inflation is a very realistic estimate.
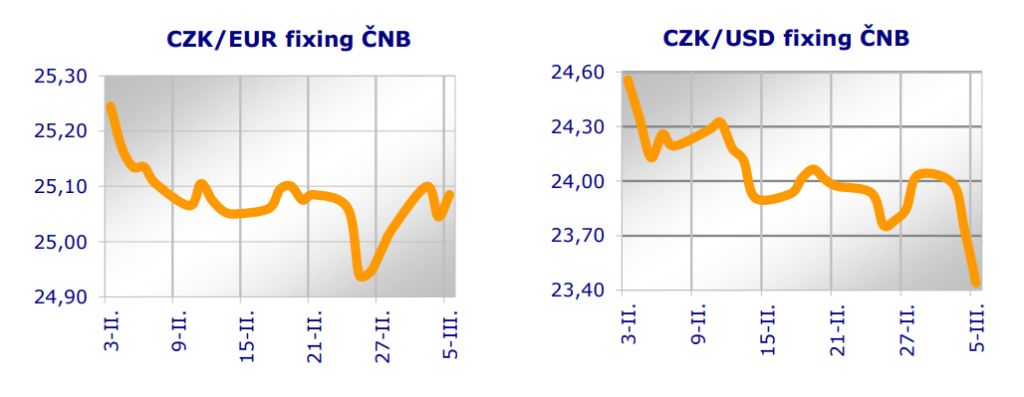
And that inflation is anything but tame, although it is easing slightly according to the latest figures, is documented by today's news that Germany is urging the EU to ease fiscal rules and increase defence spending through debt financing. Let's face it, this is nothing more than printing money. The financial market players are aware of this. Today, German bond yields have risen the most since 2022 precisely because of fears about debt financing under the new government and about money printing. This is, after all, a green light for inflation.
Markéta Šichtařová
Eurodiary 5. 3. 2025
Next Finamce s.r.o.
Nextfinance.cz
AUDIO form can be found here