Overview of the latest economic events in the Czech Republic
In the past 24 hours, the Czech government approved subsidies for coal-fired power plants under the "Lex Gas" law. The aim of this move is to support energy producers in switching to cleaner energy sources, to ensure energy security and to mitigate possible market abuse.
In addition, the Czech Statistical Office reported a decline in industrial production in November, which points to persistent problems in the manufacturing industry. Analysts suggest that the decline may continue, highlighting the need for strategic interventions to revive industrial growth.
Foreign investment - trends and attractions: 24-hour overview The Czech Republic continues to attract foreign investment, especially in the energy and retail sectors. Polish energy conglomerate Orlen has announced plans to invest CZK 1 trillion in gas and power projects, signalling confidence in the potential of the Czech energy market.
Important events from the Czech Republic
The Czech e-commerce sector is showing signs of recovery after two years of decline. E-shop sales in 2024 reached CZK 194 billion, indicating renewed consumer confidence and adaptation to digital retail platforms. However, the number of e-stores has declined, indicating market consolidation. In the automotive sector, Skoda Auto introduced a new version of its electric SUV, Enyaq. Notably, the company has stopped producing its most affordable variant, reflecting a change in market strategy and consumer demand for higher-end models.
Significant events outside the Czech Republic with global impact
The European automotive industry is facing challenges globally as a result of stricter emission regulations set by the European Commission. Car manufacturers are under pressure to meet these standards or face heavy fines, prompting calls for changes to the regulations to give the industry more time to comply. In addition, geopolitical tensions have led the Czech Republic to close its airspace to Russian airlines, thereby complying with wider European measures. These measures underline the interdependence of global politics and economic policies, with potential implications for international trade and travel.
Overview of the main macroeconomic indicators from the Czech Republic: January 2025
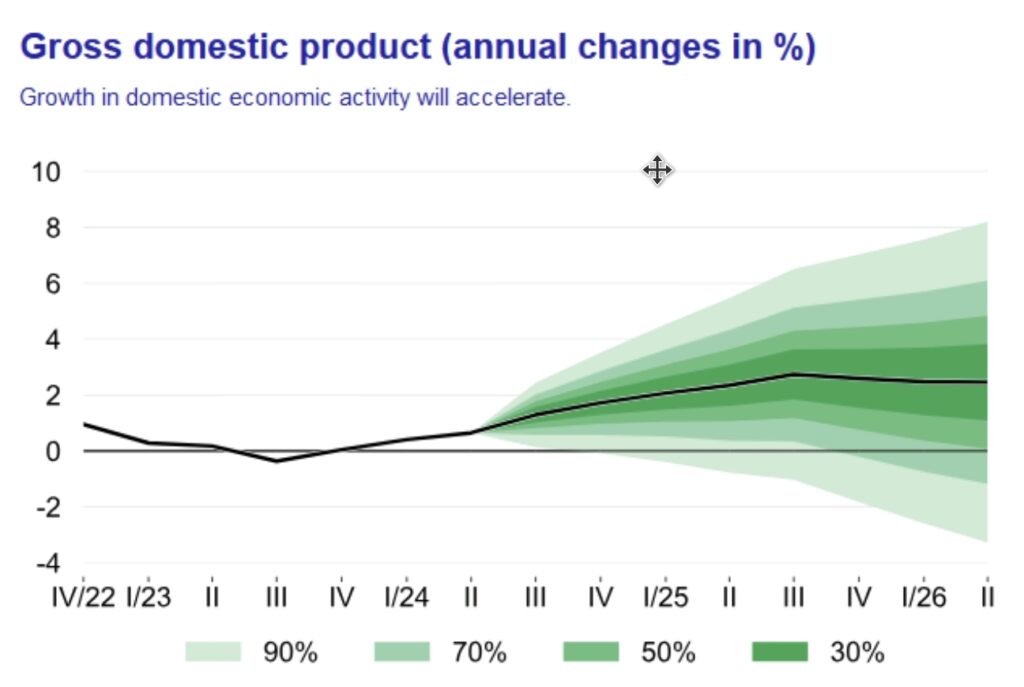
HDP Q3 1,4%
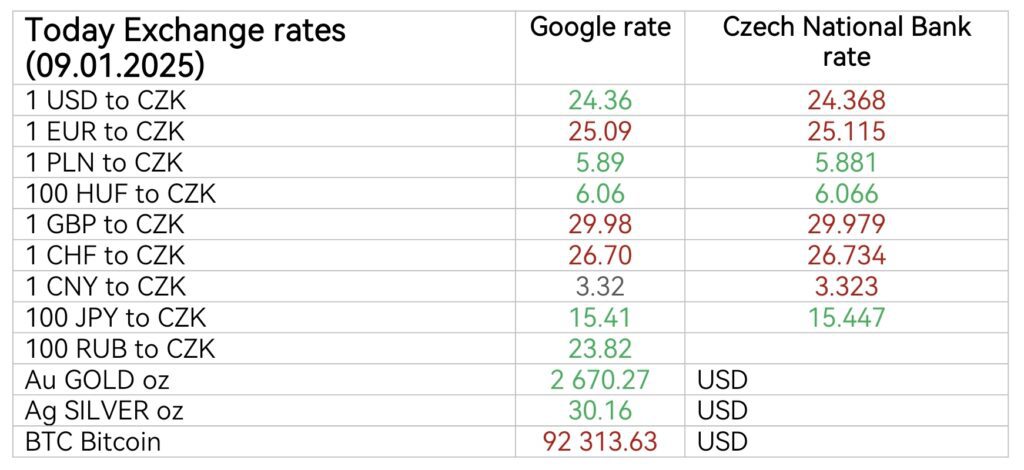
Latest GDP forecast by the Czech National Bank: (annual GDP change)
2024: 1.0 %
2025: 2.4 %
2026: 2, 4 %
HDP: 342 990 000 000 USD
GDP per capita: 33 040 USD
GDP purchasing power parity: 645 540 000 000 USD
Average gross nominal wage Q3 2024: 45 412 CZK (+7%)
Minimum wage: 20 800 CZK

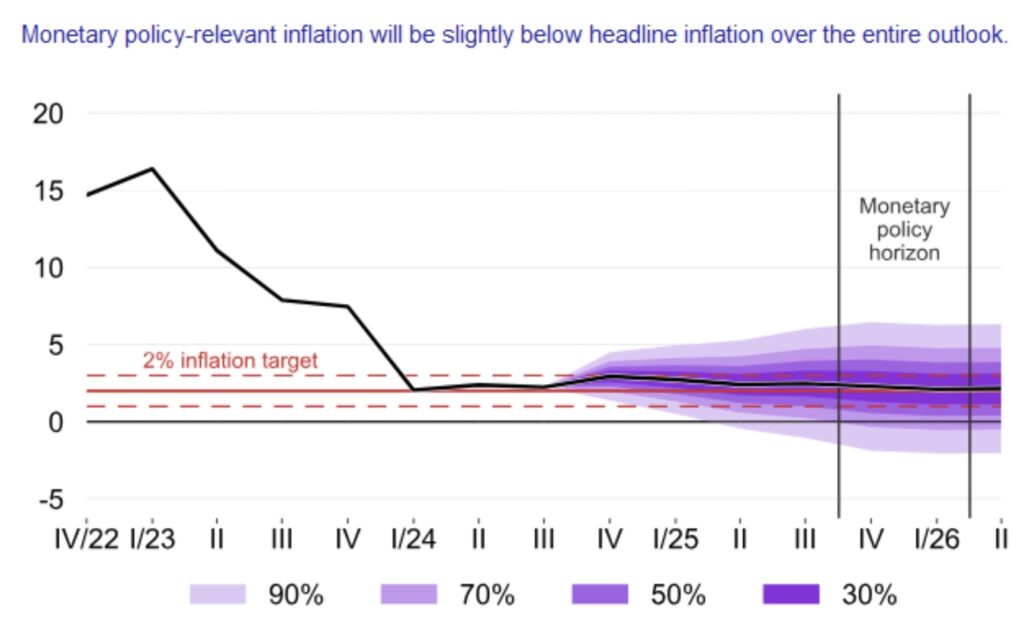
Interest rate (December 2024): 4%
Inflation rate - consumer price index (annual) 2.8 %
Inflation rate - consumer price index (month-on-month) 0.1 %
Average annual inflation (2023): 10.7% (2022: 15.7%)
Industrial producer price index (annual) 1.7 %
Market services price index (annual) 3.7 %
Construction work price index (annual) 2.5 %
Agricultural producer price index (annual) 5.5 %
Money supply M3 (October 2024): 7 002 614 340 000 CZK
Money supply M3 (2002): CZK 1 339 928 850 000
(M3 reflects the total amount of money in circulation in the economy)
Deficit/surplus of public finances Q3 2024: -34 406 000 000 CZK
Consolidated public debt Q3 2024: CZK 3,449,937,000,000
Population 2024/9: 10 897 237
Total number of economic operators 2023: 2 800 294
Number of economic entities with identified activity 2023: 1 668 516
Number of natural persons in business 2023: 1 968 473
Sources:
Czech Statistical Office, official website accessed 3.1.2025, https://csu.gov.cz/
Czech National Bank, official website, accessed 3.1.2025, https://www.cnb.cz/
Czech National Bank - Monetary Policy Report - Autumn 2024 page 19, accessed 28.12.2024
International Monetary Fund, official website, accessed 4 January 2025, https://www.imf.org/
GH
photo: wikipedia commons




3 comments
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.