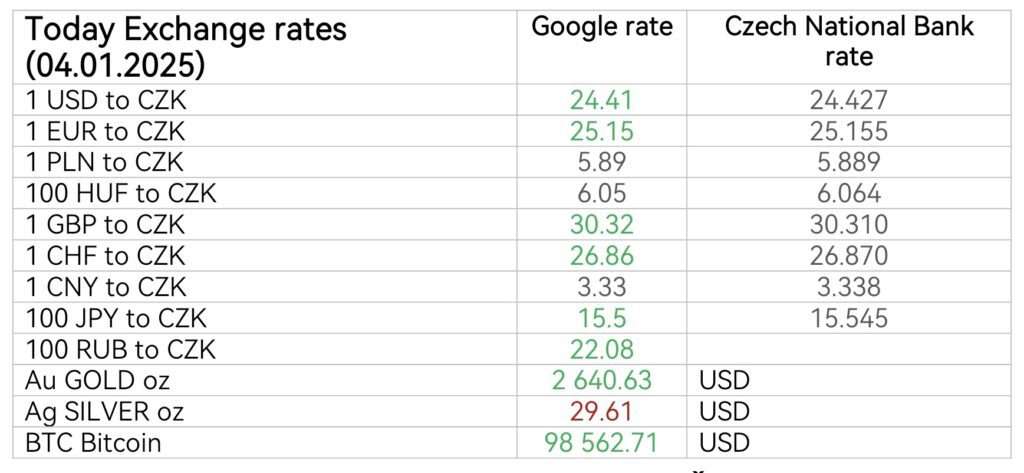
Overview of the latest economic events in the Czech Republic
The Czech economy is struggling with rising energy costs despite being a leading exporter of electricity. Household electricity prices have risen significantly, creating a paradox in the domestic energy market. Meanwhile, Volkswagen has launched an aggressive cost-cutting programme, the most stringent in its history, to cope with the challenges of switching to electric vehicles while maintaining profitability.
Foreign investment trends: 24-hour overview
Foreign investment in the Czech Republic remains strong, particularly in the renewable energy and automotive sectors. International players are channelling resources into solar and wind energy projects, in line with the country's green transformation goals. In addition, global car manufacturers are taking advantage of the Czech Republic's strategic location and skilled workforce to boost production and innovation in the field of electromobility, further strengthening the country's role in the European market.
Important events from the Czech Republic
Energy security continues to dominate economic discussions and the government is focusing on diversifying energy sources in the context of reduced gas imports from Russia. In addition, the growing adoption of electric vehicles and infrastructure development shows that the country can adapt to global trends. The resilience of the Czech economy, reflected in the strong stock market performance and sustained foreign investment, underlines its ability to deal effectively with the ongoing challenges.
Significant events outside the Czech Republic with global impact
Analysts predict that commodity prices in 2025 will be affected by geopolitical tensions and economic growth. Gold prices have risen sharply due to increased central bank purchases related to conflicts, while oil prices are expected to average between $65 and $79.9 per barrel, which will be influenced by increases in non-OPEC production and China's economic health.
Following President Trump's re-election, advisers are pushing for industrial policy and trade controls to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers. This marks a shift away from traditional free-market economics towards protectionism, with possible implications for global trade.
Overview of the main macroeconomic indicators from the Czech Republic: January 2025
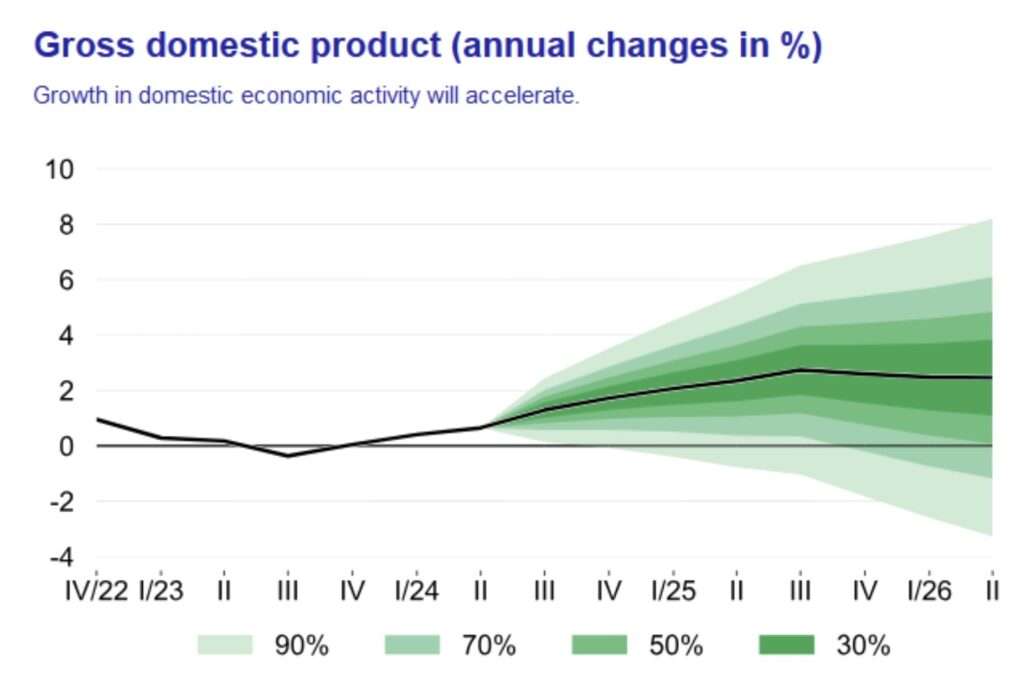
HDP Q3 1,4%
Latest GDP forecast by the Czech National Bank: (annual GDP change)
2024: 1.0 %
2025: 2.4 %
2026: 2, 4 %
HDP: 342 990 000 000 USD
GDP per capita: 33 040 USD
GDP purchasing power parity: 645 540 000 000 USD
Average gross nominal wage Q3 2024: 45 412 CZK (+7%)
Minimum wage: 20 800 CZK
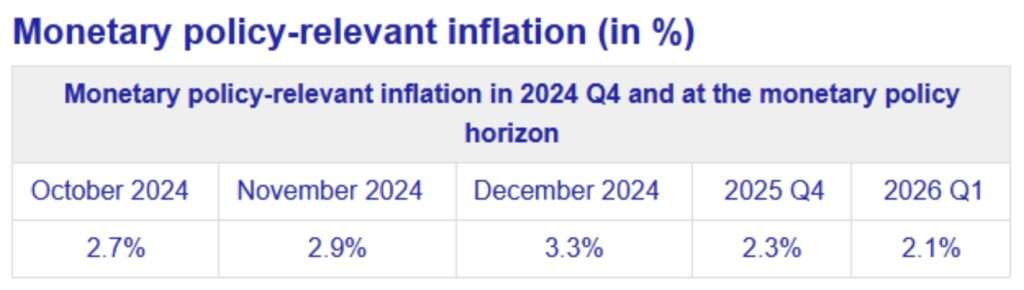
Interest rate (December 2024): 4%
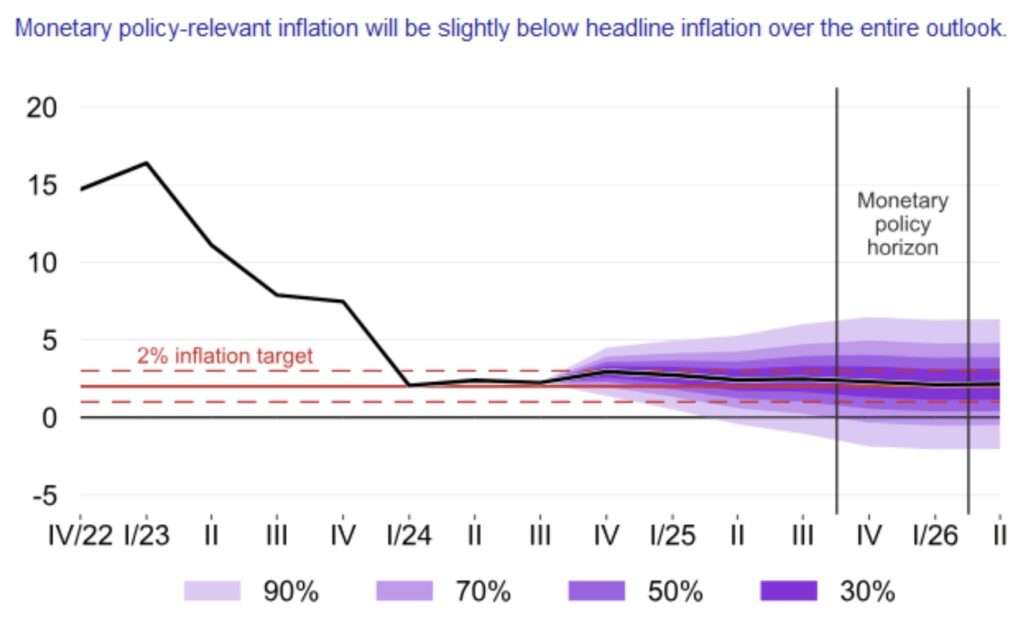
Inflation rate - consumer price index (annual) 2.8 %
Inflation rate - consumer price index (month-on-month) 0.1 %
Average annual inflation (2023): 10.7% (2022: 15.7%)
Industrial producer price index (annual) 1.7 %
Market services price index (annual) 3.7 %
Construction work price index (annual) 2.5 %
Agricultural producer price index (annual) 5.5 %
Money supply M3 (October 2024): 7 002 614 340 000 CZK
Money supply M3 (2002): CZK 1 339 928 850 000
(M3 reflects the total amount of money in circulation in the economy)
Deficit/surplus of public finances Q3 2024: -34 406 000 000 CZK
Consolidated public debt Q3 2024: CZK 3,449,937,000,000
Population 2024/9: 10 897 237
Total number of economic operators 2023: 2 800 294
Number of economic entities with identified activity 2023: 1 668 516
Number of natural persons in business 2023: 1 968 473
Sources:
Czech Statistical Office, official website accessed 3.1.2025, https://csu.gov.cz/
Czech National Bank, official website, accessed 3.1.2025, https://www.cnb.cz/
Czech National Bank - Monetary Policy Report - Autumn 2024 page 19, accessed 28.12.2024
International Monetary Fund, official website, accessed 4 January 2025, https://www.imf.org/
GH
photo: epet.cz