U.S. policy is gradually discouraging its allies from using U.S. AI technologies. This trend is leading to a growing interest in so-called sovereign AI, the ability of individual states to gain access to AI technologies without relying on foreign powers. While this development weakens US influence, it may also strengthen competition and support for open technologies.
The United States is behind the creation of the transistor, the Internet, and the transformer architecture that powers modern artificial intelligence. It has long been one of the technological superpowers. Yet the actions of several US administrations in recent years have caused many countries to fear over-reliance on US technology.
Sanctions and export restrictions have caused mistrust
In 2022, after the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the United States imposed sanctions on banks linked to Russian oligarchs. However, the side effect of these measures also affected ordinary consumers, whose credit cards were blocked. Then, shortly before the end of its mandate, the Joe Biden administration imposed export restrictions known as „AI diffusion“, which limited the ability of many countries - including US allies - to purchase advanced AI chips.
During Donald Trump's presidency, the „America First“ policy has accelerated this trend. The United States has introduced extensive and often chaotic tariffs not only against rivals, but also against allies. Tensions have also been raised by statements about a possible takeover of Greenland or a tough approach to migration. Criticism has also been levelled at ICE's crackdown on immigration authorities, which according to some reports has led to violent incidents and the deaths of several people. Footage of the ICE crackdown has spread through the world's media and critics say it has damaged the image of the United States, leading some foreign professionals to fear travel to the US.
Sovereign AI as a strategic priority
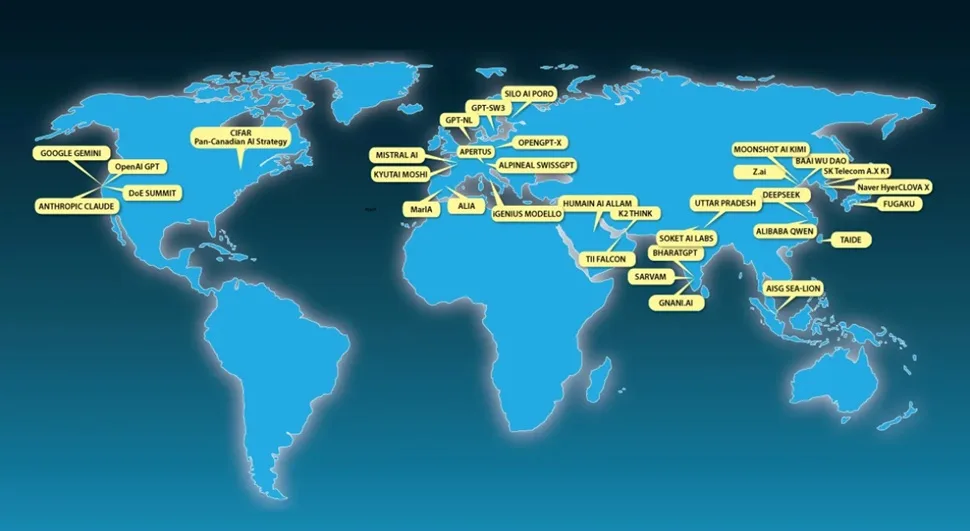
Given the strategic importance of AI, states want to ensure that no foreign power can interrupt their access to this technology. This is why the concept of sovereign AI is emerging.
This concept is not yet precisely defined and complete technological independence is almost impossible in practice. Advanced AI chips are still designed in the US and manufactured mostly in Taiwan, while much of the power equipment and computer hardware comes from China. Yet there are growing efforts to create alternatives to the most advanced models from US companies OpenAI, Google and Anthropic.
This is partly why Chinese open-weight models such as DeepSeek, Qwen, Kimi and GLM are rapidly gaining popularity, especially outside the United States.
Open source software as a path to independence
Sovereign AI doesn't have to mean that every country builds an entire tech ecosystem on its own. By engaging in the global open source community, countries can ensure access to modern technologies without having complete control over them. The goal is not to control the entire system, but to prevent anyone else from controlling it.
A similar principle already works for software like Linux, Python or PyTorch. No country fully controls these projects, but at the same time no one can stop others from using them.
This trend is motivating governments to invest more in open models. The United Arab Emirates, for example, recently introduced an open source model, K2 Think. India, France, South Korea, Switzerland and Saudi Arabia are also developing their own language models. Many other countries are also building their own computing infrastructure or sharing it with trusted partners.
Fragmentation may bring more competition
The growing mistrust among democratic countries is a negative trend. Yet it can also have positive effects. History shows that global technological dominance can be disrupted by local players. While Google and Bing dominate global search, Baidu has succeeded in China and Yandex in Russia.
If countries start to support their own technology companies more, a wider range of competitive companies can emerge. This could slow down market monopolisation while encouraging innovation. Moreover, for many countries, participation in open source projects is the cheapest way to keep up with technological developments.
Davos highlighted the change in global approach
At the recent World Economic Forum in Davos, many business and government officials said that their willingness to rely on US technology suppliers is declining. At the same time, demand for alternatives is growing.
Paradoxically, the America First policy may ultimately contribute to a wider global diffusion of AI and greater technological diversification.
deplearning.ai/gnews.cz - GH